Esophageal manometry
An important investigation for Esophageal motility disorders
sophageal manometry is a test used to measure the function of the lower esophageal sphincter and the muscles of the esophagus. Lower esophageal sphincter or LES is the valve that prevents reflux (coming back) of gastric acid into the esophagus. Esophageal manometry measures the rhythmic muscle contractions that occur in your esophagus when you swallow. Esophageal manometry also measures the coordination and force exerted by the muscles of your esophagus. This investigation will tell your doctor if your esophagus is able to move food to your stomach normally. To know why you might be experiencing a problem with your digestive system, it helps to understand the swallowing and digestive processes. The manometry test is commonly given to people who have: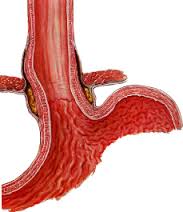
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain when swallowing
- Heartburn
- Chest pain
- Regurgitation (food coming back to throat)
Manometry is also mandatory as a part of 24 hour pH or pH and Impedance study. Adroit Clinic is one of the very few places where this investigation facilities are available in India. Dr Chirag Thakkar has a wide experience of performing this test and managing the esophageal motility disorders.
The swallowing processes and possible problems with it
When you swallow, food moves down your esophagus and into your stomach with the assistance of a wave-like motion called peristalsis or contractions. Disruptions in this wave-like motion may cause chest pain or problems with swallowing.
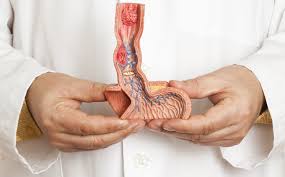 In addition, the muscular valve connecting the esophagus with the stomach, called the esophageal sphincter, prevents food and acid from backing up out of the stomach into the esophagus. If this valve does not close properly after swallowing, food and stomach acids can enter the esophagus and cause a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Also if the valve does not open properly during swallowing this may lead to a condition called Achalasia Cardia in which you have difficulty in swallowing.
In addition, the muscular valve connecting the esophagus with the stomach, called the esophageal sphincter, prevents food and acid from backing up out of the stomach into the esophagus. If this valve does not close properly after swallowing, food and stomach acids can enter the esophagus and cause a condition called gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Also if the valve does not open properly during swallowing this may lead to a condition called Achalasia Cardia in which you have difficulty in swallowing.
Manometry will indicate not only how well the esophagus is able to move food down the esophagus but also how well the esophageal sphincter is working to allow swallowing and prevent reflux.
Preparation for the test Disclose your medical conditions
Tell the physician if you have a lung or heart condition, have any other diseases, or have allergies to any medication or if your are pregnant.
Let the doctor performing manometry know about your regular medications
 Since many medications can affect esophageal pressure and the natural muscle contractions required for swallowing, be sure to discuss with your healthcare professional each medication you are taking. Your doctor may ask that you temporarily stop taking one or more medications before your test.
Since many medications can affect esophageal pressure and the natural muscle contractions required for swallowing, be sure to discuss with your healthcare professional each medication you are taking. Your doctor may ask that you temporarily stop taking one or more medications before your test.
Day of test
Eating and drinking
- Do not eat or drink anything 4 to 6 hours before the test.
During the test
- You are not sedated. However, a topical anesthetic (pain-relieving medication) will be applied to your nose to make the passage of the tube more comfortable.
- A small, flexible tube is passed through your nose, down your esophagus and into your stomach while you swallow sips of water in sitting position. This tube is a high-resolution manometry catheter that is about 4 mm in diameter. The tube does not interfere with your breathing. You will be seated while the tube is inserted.
- You may feel some discomfort as the tube is being placed, but it takes only about a minute to place the tube. Most patients quickly adjust to the tube’s presence. Vomiting and coughing are possible when the tube is being placed, but are rare.
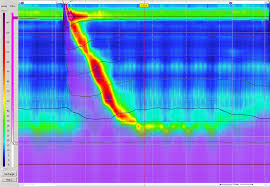
- After the tube is inserted, you will be asked to lie on your left side. The end of the tube exiting your nose is connected to a machine that records the pressure exerted on the tube. Sensors at various locations on the tubing sense the strength of the lower esophageal sphincter and muscles of the esophagus. During the test, you will be asked to swallow a small amount of water to evaluate how well the sphincter and muscles are working. Once the test begins it is important to breathe slowly and smoothly, remain as quiet as possible and avoid swallowing unless instructed to do so. The sensors also measure the strength and coordination of the contractions in the esophagus as you swallow.
- The test lasts 15-30 minutes. When the test is over, the tube is removed. Your doctor will interpret the recordings that were made during the test.
After the test
- Clinic will notify you when the test results are available or will discuss the results with you at the end of the procedure.
- You may resume your normal diet and activities and any medications that were withheld for this test.
- You may feel a temporary soreness in your throat. Lozenges or gargling with salt water may help.
- If you think you may be experiencing any unusual symptoms or side effects, call your doctor.
What are the risks with this study?
There are no major risks attached to the procedure. Some patients may experience minor discomfort in the throat, nose and occasionally develop nausea and vomiting but the vast majority are able to tolerate the procedure reasonably well.
Are there any alternative tests? No alternative tests are available for this purpose.


